Russia’s foreign trade offers a fascinating glimpse into one of the world’s largest economies, showcasing its pivotal role in global commerce. With its extensive exports of energy resources and vital imports of advanced technologies, Russia navigates a complex web of international trade relationships.
This blog post delves into Russia’s trade dynamics, exploring key exports and imports, economic trends, and the country’s strategic position in the global market. Read on to uncover the intricacies of Russia’s foreign trade and understand its impact on the global economy.
Russia’s Foreign Trade
Russia’s foreign trade is a pivotal component of its economic structure, reflecting its significant role in global commerce. The country’s vast natural resources, including oil, gas, and minerals, underpin its major exports, while its import needs span a range of advanced technologies and essential goods. Over the years, Russia has maintained a robust trade profile, characterized by substantial export volumes and a positive trade balance. The country’s trade dynamics are influenced by its geopolitical strategies, economic policies, and global market trends.
Importance in the Global Economy
Russia holds a crucial position in the global economy due to its extensive natural resource base and strategic economic relationships. As one of the world’s leading energy suppliers, Russia’s exports of crude petroleum, natural gas, and coal are vital for energy security in many countries. Additionally, Russia’s economic interactions with major global economies—such as China, the European Union, and India—highlight its integral role in international trade networks. Understanding Russia’s foreign trade not only sheds light on its economic strengths but also on its influence and dependencies within the global market.

Overview of Russia’s foreign trade
Russia’s foreign trade landscape is marked by a dynamic exchange of resources and technologies. As a major global player, Russia’s top exports include vital energy resources and industrial products, while its imports highlight a dependence on advanced technology and essential goods. This section delves into the specifics of Russia’s leading exports and imports based on the OEC database.
Top Exports of Russia
Russia is a significant player in global trade, especially in the energy sector. The country’s top exports highlight its role as a major supplier of key resources and industrial products:
- Crude Petroleum: Russia’s leading export is crude petroleum, accounting for a staggering $133 billion. This product is crucial for global energy needs and underscores Russia’s dominance in the oil market.
- Petroleum Gas: The second-largest export, petroleum gas, brings in $71.5 billion. As a primary source of energy, natural gas plays a vital role in Russia’s trade balance.
- Refined Petroleum: With exports valued at $67.4 billion, refined petroleum products are also a major contributor to Russia’s economy, reflecting the country’s advanced refining capabilities.
- Coal Briquettes: Coal briquettes, worth $36.5 billion, are another significant export. Russia’s vast coal reserves support its strong position in the global energy market.
- Gold: Russia exports gold worth $14.6 billion. As a valuable commodity, gold plays a crucial role in Russia’s trade and financial stability.
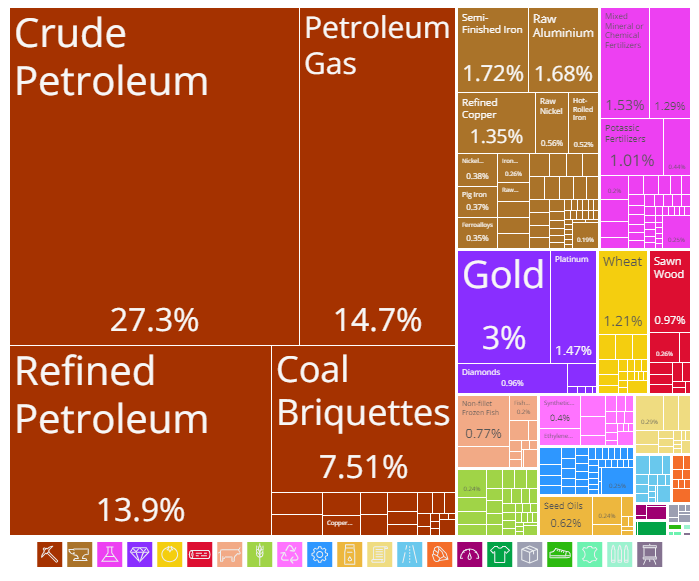
These exports are primarily directed towards key markets:
- China: $101 billion
- India: $40.4 billion
- Germany: $27.7 billion
- Turkey: $25.3 billion
- Italy: $25.1 billion

Top Imports of Russia
Russia’s import profile reflects its need for various advanced technologies and essential goods:
- Packaged Medicaments: The largest import category is packaged medicaments, valued at $9.11 billion. This reflects the demand for healthcare products and medical supplies.
- Broadcasting Equipment: With imports totaling $7.15 billion, broadcasting equipment is crucial for Russia’s media and communication infrastructure.
- Cars: Russia imports cars worth $6.38 billion, indicating a strong demand for automobiles in the domestic market.
- Computers: Importing computers valued at $3.94 billion highlights the country’s reliance on technology for business and personal use.
- Motor Vehicles; Parts and Accessories: At $3.64 billion, this category includes various vehicle parts essential for the automotive industry.
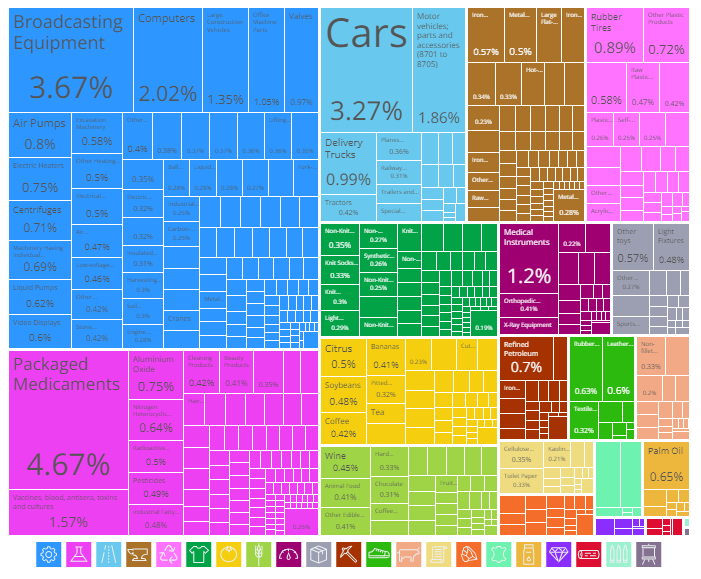
The major suppliers of these imports are:
- China: $75.4 billion
- Germany: $15.5 billion
- Turkey: $9.24 billion
- Kazakhstan: $8.78 billion
- South Korea: $6.33 billion

Review of Russia’s Foreign Trade and Economic Performance (2004–2024)
1. Historical Trade Data (2004–2021)
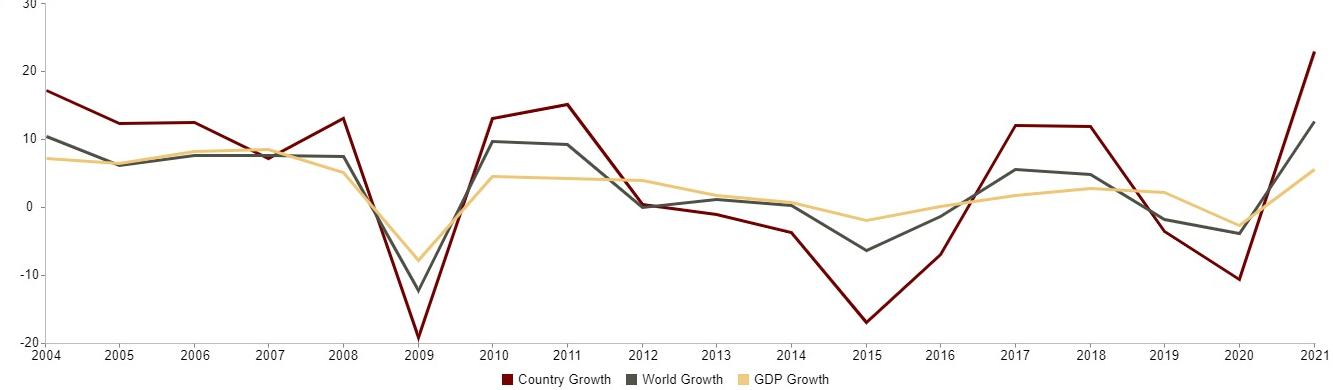
According to the World Integrated Trade Solution (WITS), from 2004 to 2021, the Russian Federation achieved substantial trade figures. The country recorded total exports amounting to $492.31 billion and total imports of $293.50 billion, resulting in a positive trade balance of $198.82 billion. The Effectively Applied Tariff Weighted Average was 4.17%, while the Most Favored Nation (MFN) Weighted Average tariff was 5.11%. During this period, Russia’s trade growth was 22.86%, outpacing the global average growth rate of 12.59%. The GDP for the Russian Federation was approximately $1.84 trillion. Exports and imports of goods and services were significant, with exports constituting 29.89% of GDP and imports at 20.66%. Services exports were valued at $55.55 billion, and services imports at $75.93 billion.
2. Economic Standing in 2022
According to OEC, in 2022, Russia was ranked as the 8th largest economy globally in terms of GDP (current US$), the 12th largest in total exports, and the 30th in total imports. The country was positioned 63rd in GDP per capita and 47th in the Economic Complexity Index (ECI), reflecting its diverse economic profile and complexity.

3. Recent Economic Developments (2023–2024)
As reported by Trading Economics, Russia’s GDP grew by 3.6% in 2023, rebounding from a 1.2% contraction in 2022. This recovery was largely driven by state-funded arms and ammunition production due to the ongoing Ukraine conflict, with a significant portion of industrial output growth attributed to this sector. Key areas of growth included manufacturing (7% vs. -2% in 2022), wholesale and retail trade (7.3% vs. -12.8%), transportation (3.2% vs. 0.1%), hospitality (10% vs. 5.1%), information and communication (10% vs. 0.9%), and financial services (8.6% vs. 2.4%). Household consumption and fixed investment also saw notable increases.
Looking ahead to 2024, Russia’s economy minister forecasts a 2.3% growth, which is slightly below the IMF’s projection of 2.6%, indicating a moderated but positive economic outlook.
Conclusion
Russia’s foreign trade highlights its significant role in the global economy, driven by major exports of energy resources and industrial products. Its strategic trade relationships and positive trade balance underscore its influence and adaptability in international markets. As Russia navigates economic and geopolitical shifts, its trade patterns will continue to reflect its global economic position and impact. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for grasping Russia’s role in the world economy.
At GTC, we specialize in managing the complexities of Russia’s vibrant foreign trade. Whether you’re importing critical technologies or exporting valuable resources, our expert team ensures smooth and efficient logistics solutions tailored to your needs. Contact us today to streamline your international shipments and leverage our deep understanding of Russia’s trade landscape. Let’s optimize your supply chain and drive your global success together!






